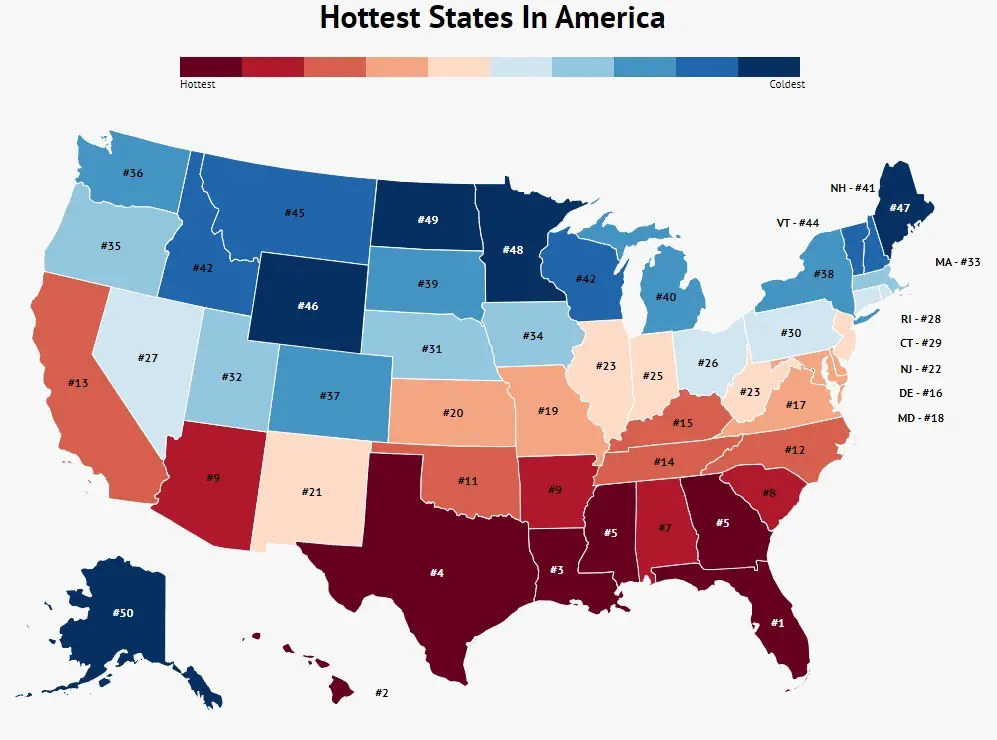
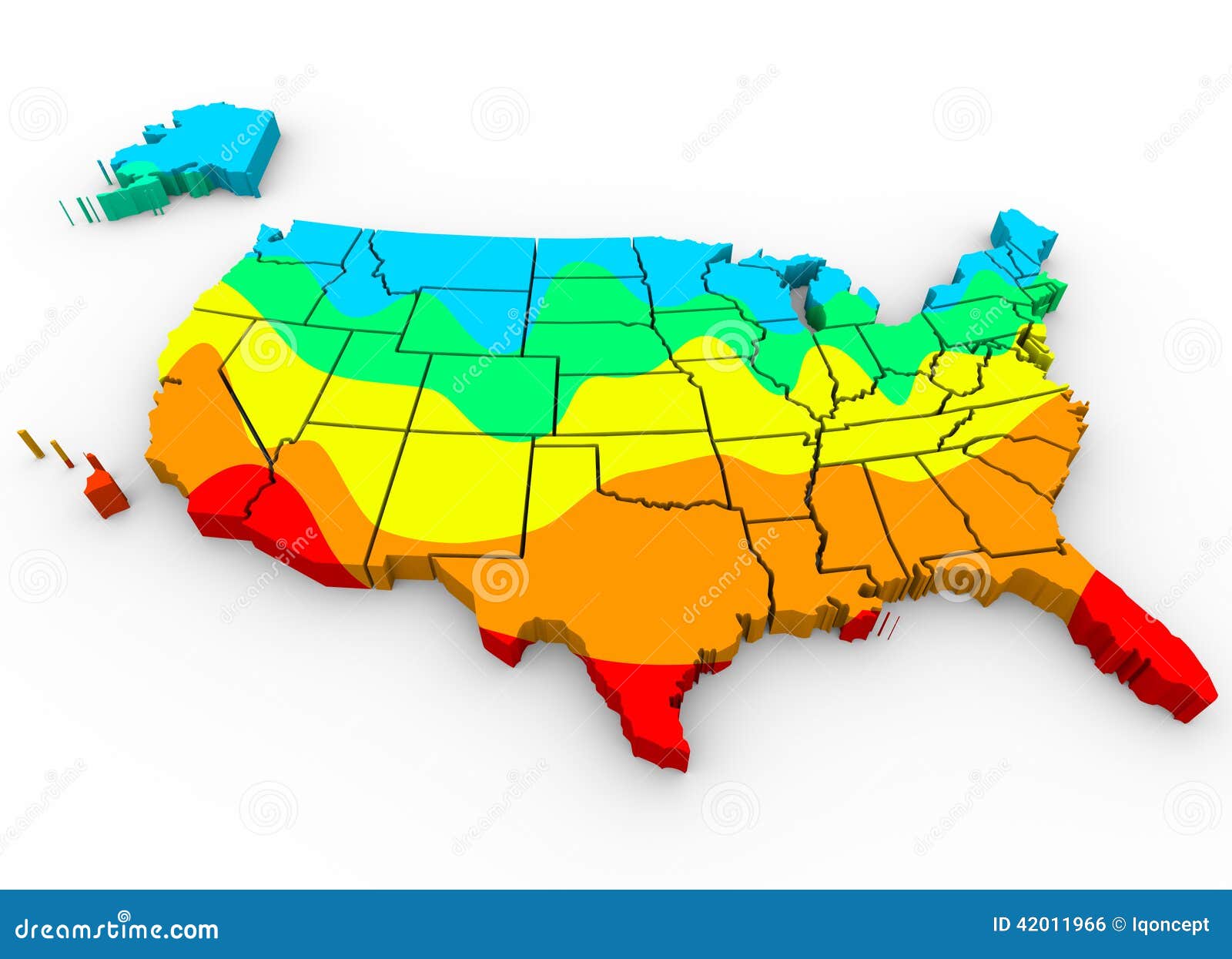
When it comes to the hottest state in the United States, Arizona often takes the crown for its scorching desert climate and record-breaking temperatures. Known for its blazing sun, arid landscapes, and unique ecosystems, Arizona is a place where heat dominates much of the year. But what makes Arizona stand out as the hottest state, and how does its climate compare to other regions in the U.S.? This article will delve into the factors that contribute to Arizona's extreme heat, its impact on daily life, and the ways people adapt to survive in such conditions.
Many people associate the southwestern United States with intense heat, and for good reason. Arizona, in particular, holds several records for high temperatures, making it a fascinating yet challenging place to live. From its expansive deserts to its urban centers like Phoenix, the state experiences some of the highest temperatures recorded in the country. Understanding why Arizona is so hot and how this affects its residents can provide valuable insights into climate science and human adaptation.
In this article, we will explore the hottest state in the United States, focusing on Arizona's climate, its geographical features, and the implications of living in such an environment. By examining temperature patterns, historical records, and the impact of global warming, we aim to give readers a comprehensive understanding of why Arizona earns its reputation as the hottest state in the nation.
Read also:Is Luke Bryan A Trump Supporter Exploring The Country Stars Political Views
Understanding the Climate of the Hottest State in the United States
Arizona's Unique Desert Climate
Arizona's desert climate plays a significant role in making it the hottest state in the United States. The state is home to two major deserts: the Sonoran Desert in the south and west, and the Mojave Desert in the northwest. These deserts contribute to Arizona's extreme heat, with temperatures often soaring above 100°F (38°C) during the summer months.
Desert climates are characterized by low humidity, minimal rainfall, and intense sunlight. In Arizona, these conditions create a perfect storm for high temperatures. The lack of moisture in the air means that heat is retained more effectively, leading to hotter days and cooler nights. This diurnal temperature variation is a hallmark of desert climates and contributes to the state's reputation as a hot and arid region.
Temperature Patterns in Arizona
Arizona's temperature patterns are influenced by its location and elevation. The state's southern and western regions experience the highest temperatures, with cities like Phoenix and Yuma often recording temperatures above 110°F (43°C) during the summer. In contrast, areas with higher elevations, such as Flagstaff, tend to have milder temperatures due to their altitude.
One of the most notable features of Arizona's climate is the monsoon season, which occurs from July to September. During this period, moisture from the Gulf of California and the Gulf of Mexico brings periodic thunderstorms and rainfall to the state. While these storms can provide temporary relief from the heat, they also contribute to flash flooding and other weather-related challenges.
Record-Breaking Temperatures in the Hottest State
Arizona's Extreme Heat Records
Arizona holds several records for extreme heat, solidifying its status as the hottest state in the United States. On June 26, 1990, the city of Lake Havasu recorded a temperature of 128°F (53°C), one of the highest temperatures ever recorded in the country. Additionally, Phoenix consistently ranks among the hottest cities in the U.S., with an average of over 100 days per year where temperatures exceed 100°F (38°C).
These record-breaking temperatures highlight the challenges faced by Arizona's residents and infrastructure. Extreme heat can lead to heat-related illnesses, power outages, and increased water consumption, all of which require careful planning and management to mitigate their effects.
Read also:Dr Patrick Mbatha A Renowned Medical Professional And His Remarkable Journey
Comparing Arizona's Heat to Other States
While Arizona is widely regarded as the hottest state in the United States, other states like California, Nevada, and Texas also experience significant heat. However, Arizona's combination of high temperatures, low humidity, and prolonged heat waves sets it apart from its neighbors. For example, Death Valley in California holds the record for the highest temperature ever recorded on Earth at 134°F (56.7°C), but its location and unique geography make it an outlier rather than a representative of the state's overall climate.
In contrast, Arizona's heat is more widespread and consistent, affecting a larger portion of its population and geography. This makes it the most representative of the hottest state in the U.S.
Geographical Factors Contributing to Arizona's Heat
The Role of Elevation and Geography
Arizona's geography plays a crucial role in its extreme heat. The state's low-lying desert regions, such as the Sonoran and Mojave Deserts, are particularly susceptible to high temperatures due to their proximity to sea level and lack of vegetation. In contrast, areas with higher elevations, like the White Mountains and the Grand Canyon, experience cooler temperatures due to their altitude.
Another factor contributing to Arizona's heat is its location in the southwestern United States. This region is known for its arid climate and intense sunlight, which exacerbate the effects of heat. The state's position in the "Sun Belt" also means that it receives more direct sunlight than many other parts of the country, further increasing its temperatures.
Urban Heat Islands in Arizona
Urban areas in Arizona, such as Phoenix and Tucson, experience even higher temperatures due to the urban heat island effect. This phenomenon occurs when cities absorb and retain heat from the sun, leading to higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. The presence of concrete, asphalt, and other heat-absorbing materials in urban environments contributes to this effect, making cities like Phoenix some of the hottest places in the state.
Efforts to mitigate the urban heat island effect include planting more trees, using reflective materials in construction, and implementing green infrastructure projects. These initiatives aim to reduce the impact of extreme heat on urban populations and improve the overall livability of cities in Arizona.
Impact of Extreme Heat on Daily Life
Adapting to Life in the Hottest State
Living in the hottest state in the United States requires specific adaptations to cope with the extreme heat. Residents of Arizona have developed various strategies to stay cool and safe during the summer months. These include staying indoors during the hottest parts of the day, using air conditioning, and wearing lightweight, breathable clothing.
- Staying hydrated is crucial in Arizona's dry climate, as dehydration can occur quickly in high temperatures.
- Many businesses and schools adjust their schedules to avoid the midday heat, opening earlier and closing later to accommodate cooler temperatures.
- Outdoor activities are often scheduled for early morning or evening when temperatures are more manageable.
Heat-Related Health Concerns
Extreme heat poses significant health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing medical conditions. Heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, are common in Arizona during the summer months. To combat these risks, public health officials recommend staying cool, hydrated, and informed about weather conditions.
Local governments and organizations also provide resources and support for those affected by extreme heat, including cooling centers, hydration stations, and educational campaigns. These efforts help ensure that all residents of Arizona can stay safe and healthy during the hottest months of the year.
Environmental and Economic Impacts of Extreme Heat
Climate Change and Rising Temperatures
The effects of climate change are evident in Arizona, where temperatures have been steadily increasing over the past few decades. Rising global temperatures contribute to longer and more intense heat waves, exacerbating the challenges faced by Arizona's residents and ecosystems. Scientists predict that these trends will continue, leading to even hotter conditions in the future.
Efforts to address climate change at both local and national levels are essential to mitigating its impacts on Arizona and other regions. Implementing sustainable practices, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting renewable energy sources are just a few ways to combat the effects of global warming and protect the environment for future generations.
Economic Consequences of Extreme Heat
Extreme heat has significant economic implications for Arizona, affecting industries such as agriculture, tourism, and energy production. High temperatures can reduce crop yields, increase water consumption, and strain power grids, leading to higher costs for businesses and consumers. Additionally, the tourism industry may face challenges during the summer months when extreme heat discourages visitors from traveling to the state.
To address these economic challenges, businesses and governments must implement strategies to adapt to changing climate conditions. This includes investing in heat-resistant infrastructure, promoting water conservation, and diversifying economic activities to reduce reliance on industries vulnerable to extreme heat.
Future Prospects and Challenges
Preparing for a Warmer Future
As temperatures continue to rise, Arizona must prepare for a future characterized by even hotter conditions. This involves developing innovative solutions to address the challenges posed by extreme heat, such as improving urban planning, enhancing public health infrastructure, and promoting sustainable practices. By taking proactive steps today, Arizona can ensure that its residents and ecosystems remain resilient in the face of a changing climate.
Education and awareness are also critical components of preparing for a warmer future. By informing the public about the risks and impacts of extreme heat, Arizona can empower its citizens to take action and protect themselves and their communities. This collaborative approach will be essential in creating a sustainable and livable environment for all residents of the hottest state in the United States.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Arizona's status as the hottest state in the United States is well-deserved, thanks to its unique desert climate, record-breaking temperatures, and geographical factors. Understanding the causes and impacts of extreme heat is crucial for adapting to and mitigating its effects on daily life, the environment, and the economy. By implementing sustainable practices, promoting public health, and preparing for a warmer future, Arizona can continue to thrive despite the challenges posed by its intense heat.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about living in or visiting the hottest state in the United States. Your feedback and insights can help us better understand the complexities of extreme heat and its impact on communities around the world. Additionally, we encourage you to explore other articles on our site to learn more about climate science, human adaptation, and the fascinating world of geography.
Table of Contents